35++ Perfectly Inelastic Collision Definition
Perfectly Inelastic Collision Definition. Elastic and inelastic collisions • a collision in which the objects stick together after collision is called a perfectly inelastic collision. In this sort of collision, called a perfectly inelastic collision, the colliding objects actually end up stuck together.

Inelastic collisions, newton's laws, conservation of momentum, circular motion, frame transformations; The impulse of the collision changes the velocity of car 1, and after the collision car 1 moves with uniform velocity v 2. Elastic and inelastic collisions • a collision in which the objects stick together after collision is called a perfectly inelastic collision.
papier peint feuille de palmier noir et blanc papier peint trompe loeil industriel perforateur hilti sans fil prix pattes de scellement pour poteau
Momentum & Energy
Also after the collision, two objects stick together. What is the definition of perfectly inelastic collision?unlike an elastic collision, in which the objects stick together by conserving both momentum and kinetic energy, an inelastic collision conserves momentum, but it loses the kinetic energy. If the post collision velocity is effected by the loss, than why isn't momentum effected. Swinging balls are an example of elastic.

Perfectly inelastic collision is the case when two bodies that collide, move with the same velocity after the collision. An inelastic collision is a collision in which momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy isn't. The special case of inelastic collision is referred to as a perfectly inelastic collision. In a perfectly inelastic situation regardless of the amount of a product.

If the post collision velocity is effected by the loss, than why isn't momentum effected. Some car crashes, a collision between a meteorite and the moon, and a collision involving two balls of plasticine would be perfectly inelastic. The impulse of the collision changes the velocity of car 1, and after the collision car 1 moves with uniform velocity v.

Before the collision car 1 and mass m move with uniform velocity v 1. Swinging balls are an example of elastic. What is an elastic collision? If the post collision velocity is effected by the loss, than why isn't momentum effected. An elastic collision is a collision in which both kinetic energy and momentum is conserved.

If the post collision velocity is effected by the loss, than why isn't momentum effected. The special case of inelastic collision is referred to as a perfectly inelastic collision. Some car crashes, a collision between a meteorite and the moon, and a collision involving two balls of plasticine would be perfectly inelastic. An elastic collision is a collision in which.

What is an elastic collision? We identified it from trustworthy source. An inelastic collision, in contrast to an elastic collision, is a collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved due to the action of internal friction. An inelastic collision is a type of collision where this is a loss of kinetic energy. In this sort of collision, called a.

In collisions of macroscopic bodies, some kinetic energy is turned into vibrational energy of the atoms, causing a. An inelastic collision is a collision in which momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy isn't. If the post collision velocity is effected by the loss, than why isn't momentum effected. The special case of inelastic collision is referred to as a perfectly.

Before the collision car 1 and mass m move with uniform velocity v 1. It is represented by e and it depends upon the material of the colliding bodies. Thus, e is zero when it is perfectly inelastic collision i.e. A perfectly inelastic collision—also known as a completely inelastic collision—is one in which the maximum amount of kinetic energy has.
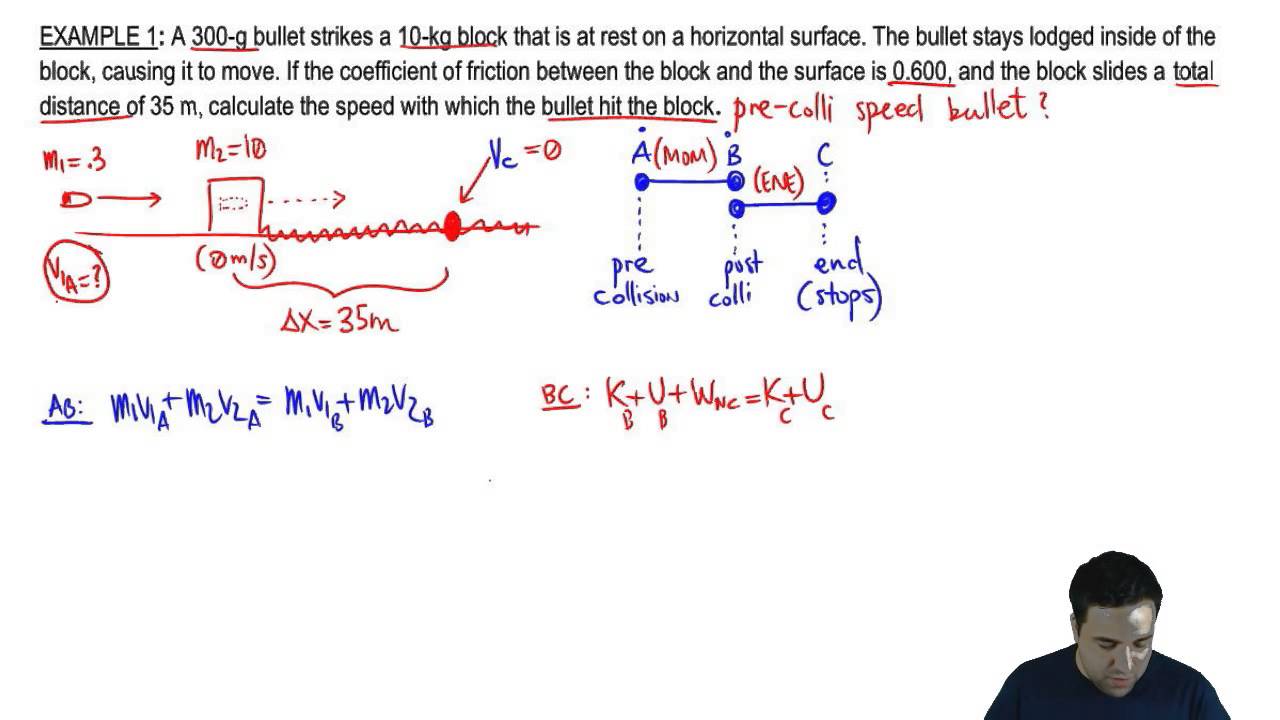
Perfectly inelastic collision is the case when two bodies that collide, move with the same velocity after the collision. For a perfectly inelastic collision, e = 0. The lost kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy, sound energy, and material deformation. A perfectly inelastic collision—also known as a completely inelastic collision—is one in which the maximum amount of kinetic energy.