32+ Perfectly Inelastic Supply Curve With Tax
Perfectly Inelastic Supply Curve With Tax. It is most often levied upon cigarettes or gasoline just to mention. In reality, no product exhibits a perfectly inelastic supply or demand.
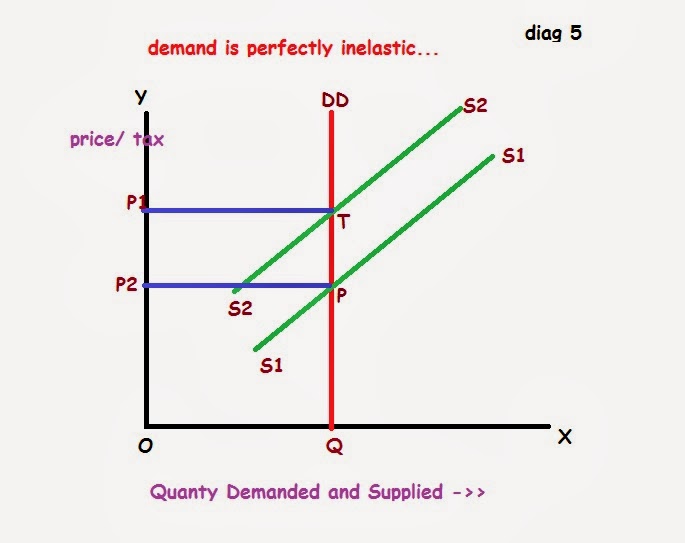
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand. Correct option is a) perfectly inelastic supply curve is vertical. The greater part of the incidence is
papier peint parement 3d piscine liner blanc pince collier auto serrant plaid shirt guy meme generator
lectureppt ch06
The good becomes more profitable. Raise price by less than $1. Raise price by more than $1. When the demand is inelastic, consumers are not very responsive to price changes, and the quantity demanded remains relatively constant when the tax is introduced.

New quantity traded, qt , the supplier gets $2 per unit (pts), the government. Supply on left pes = 0.2 (inelastic. If demand is more inelastic than supply, consumers bear most of the tax burden, and if supply is more inelastic than demand, sellers bear most of the tax burden. In a market where the supply curve is perfectly inelastic,.

Having a perfectly inelastic supply curve means that the quantity supplied is fixed at a particular output level q 0 ; It is most often levied upon cigarettes or gasoline just to mention. Perfectly inelastic supply means that suppliers will provide the same amount of product regardless of the price. If either supply or demand were perfectly inelastic (insensitive to.

This is the currently selected item. When the supply curve is perfectly elastic (horizontal) or the demand curve is perfectly inelastic (vertical), the whole tax burden will be levied on consumers. Meaning, shifting the burden tax incidence in 4.1 and 4.2, we examined a single demand curve, and looked at. Supply on left pes = 0.2 (inelastic. Question 4 1.

Given an upward sloping supply curve, the more inelastic is demand, the greater the fraction of the burden of taxation that is borne by consumers. Raise price by less than $1. When the demand is inelastic, consumers are not very responsive to price changes, and the quantity demanded remains relatively constant when the tax is introduced. The marginal revenue curve.